< |
Lazy CIP LUTs |
> |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
INTRODUCTIONThe purpose of the CIP LUTs macros is to present better views of various CIP input and output images.
The images are not changed during the application of the LUTs - the grayscale, i.e., original images can always be retrieved.
In order to actually re-calculate/correct/improve the data, the Lazy View and Handle macro is required.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
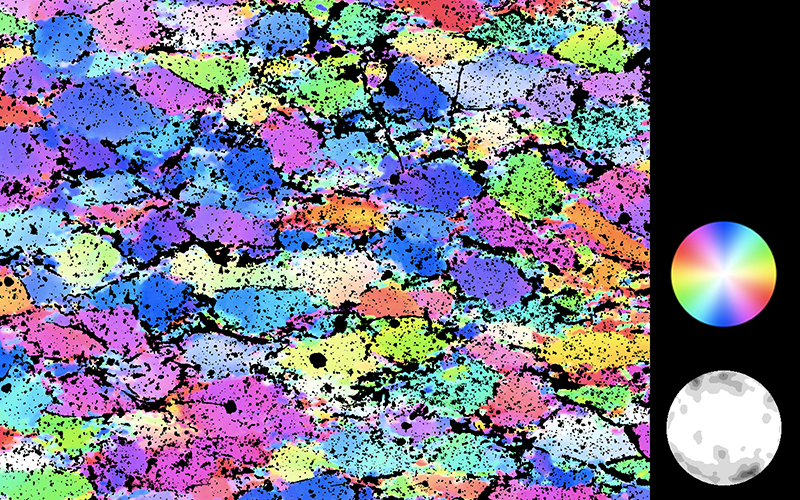
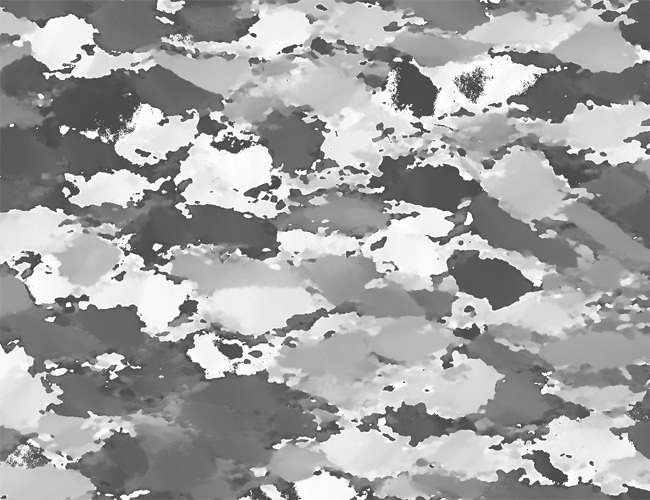
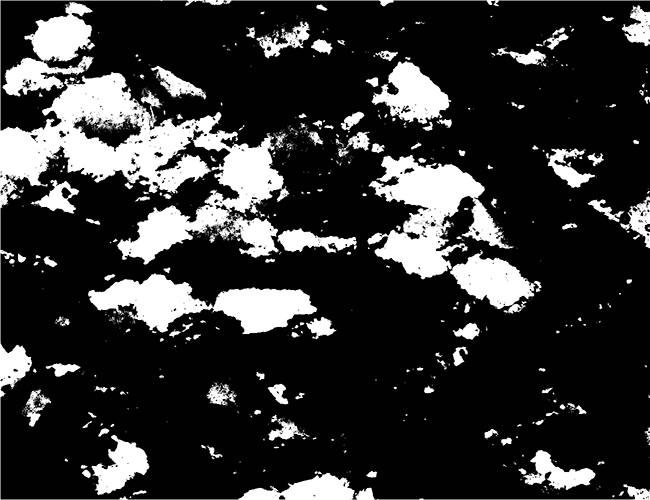
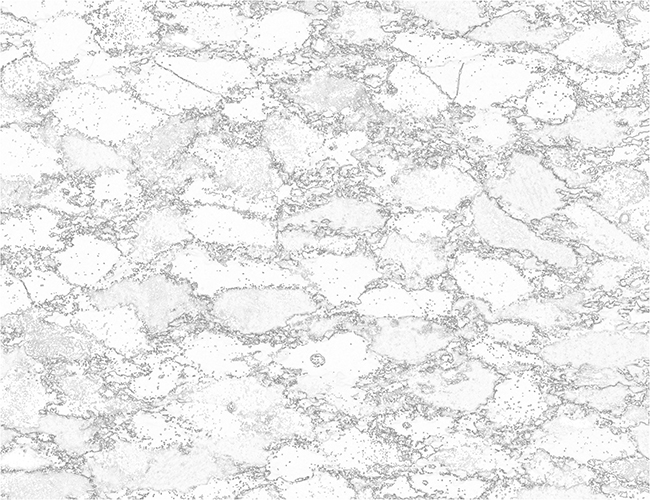
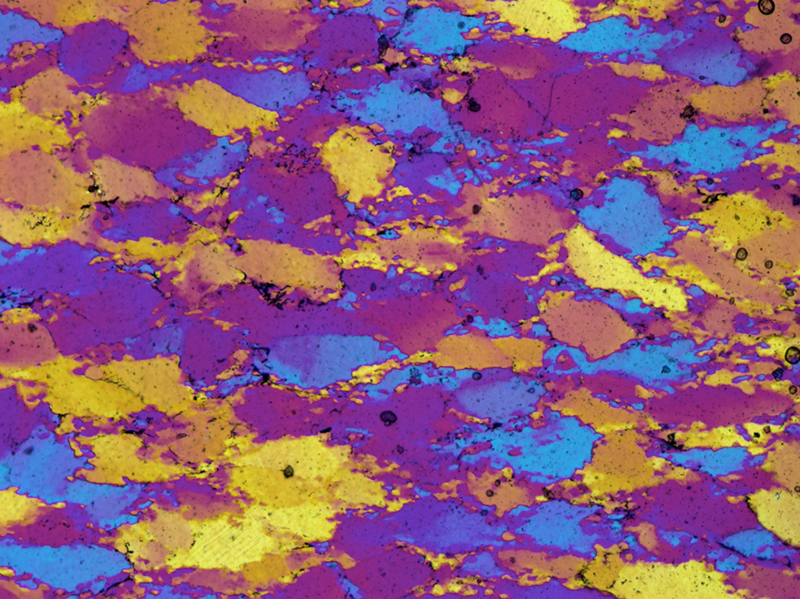
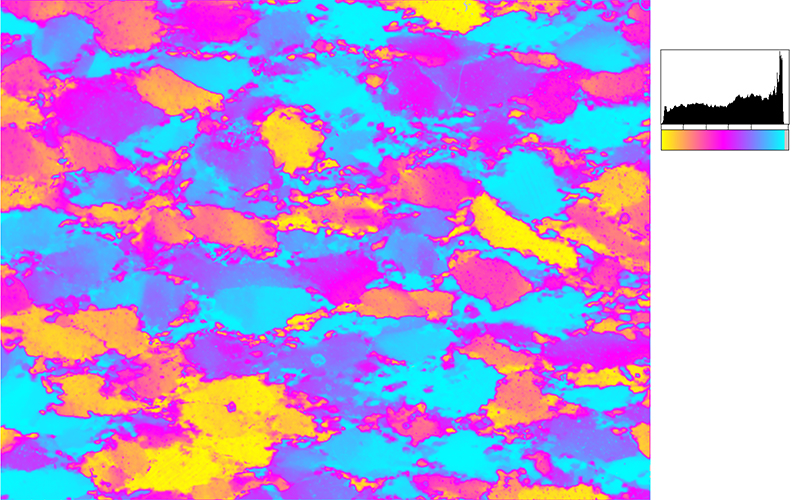
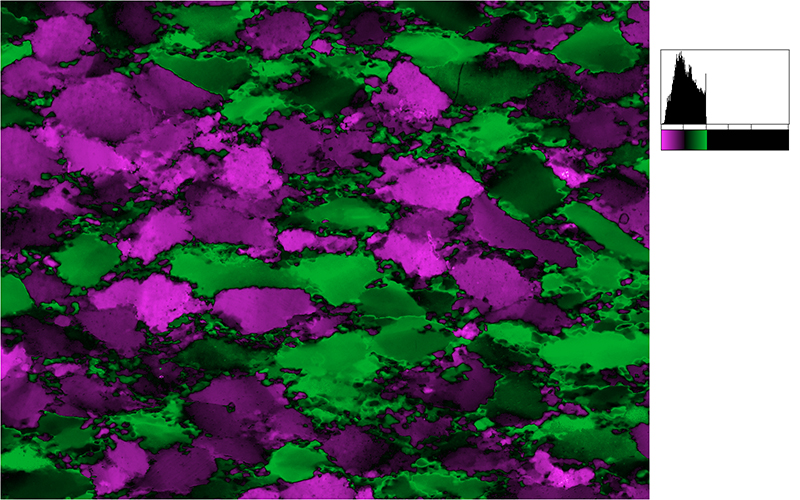
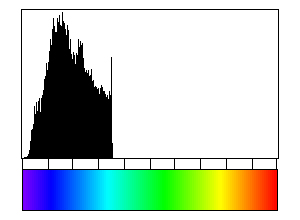
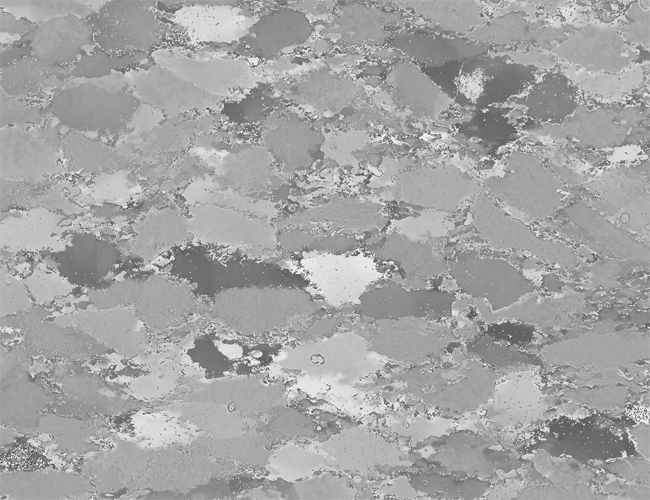
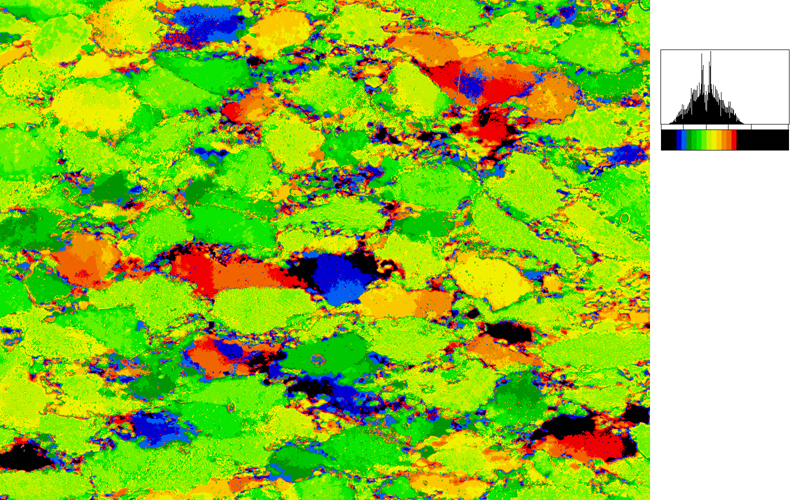
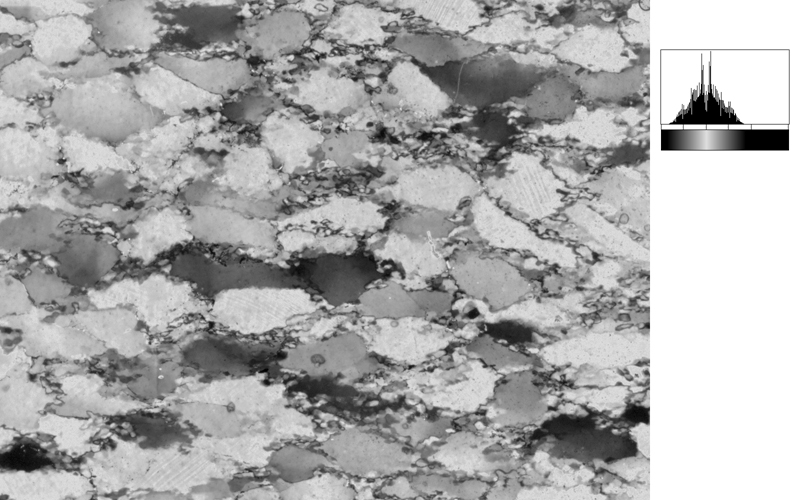
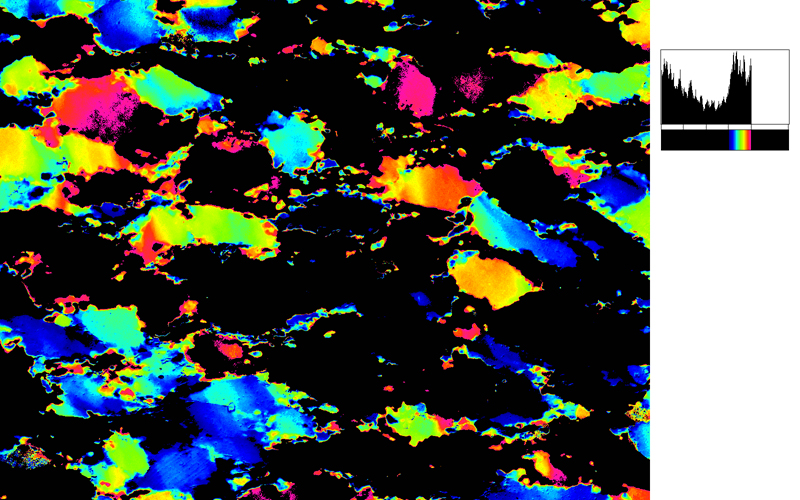
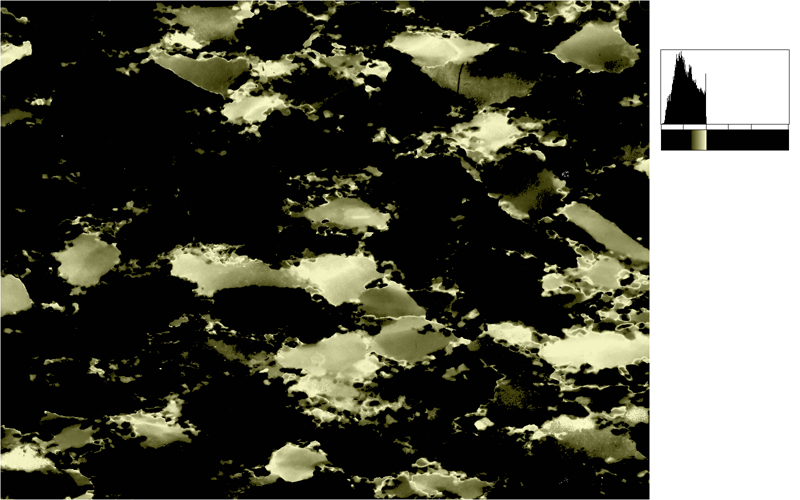
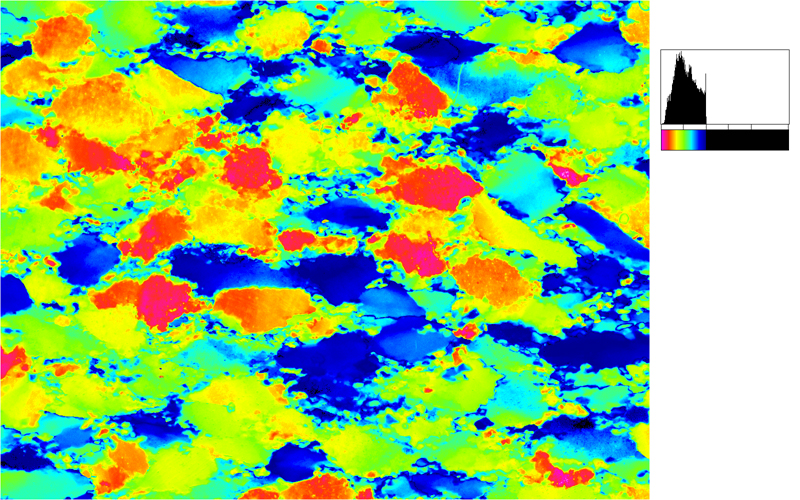
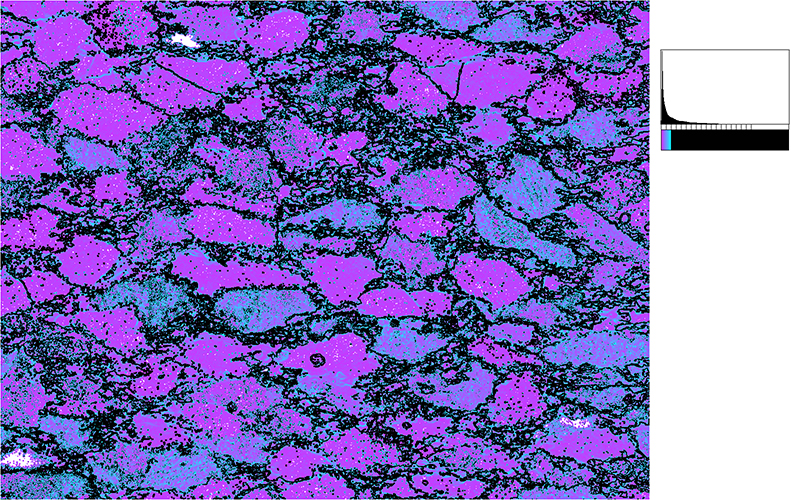
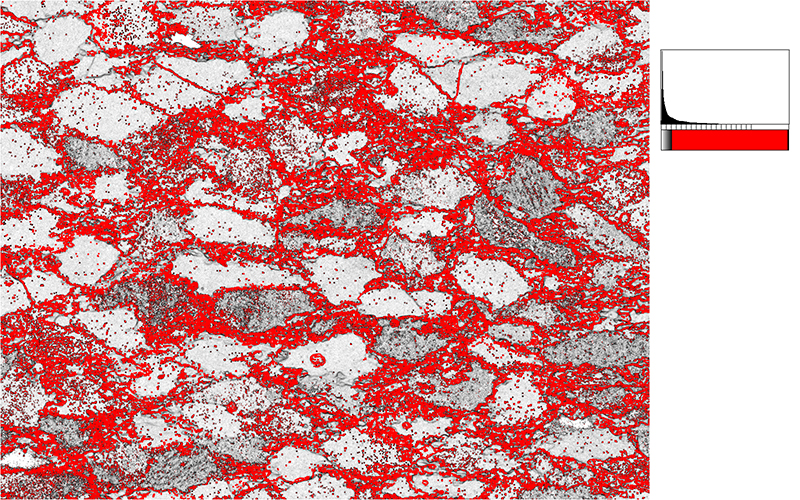
Two typical examples for CIP LUT applications are shown on the left: Before beginning the CIP calculation, it may be useful to check input images. The rotation image (taken with crossed polarizers, the lambda plate inserted and a red interference filter applied) can be viewed with coloring similar to what one would observe when looking at the section without the interference filter. For a quick check, if the image is oriented correctly, it may be useful to use [+] or [-] to convert a monochrome rotation image of an optically positive or a negative mineral (quartz or calcite, respectively) to a color image showing - at least in an approximate manner - the blue and the yellow orientaions. (Compare with original). After the CIP calculation, the different result files have to be evaluated. Here, the misorientaion file w/r to North is shown. The values span a range of (0° ≤ angle ≤ 180°). Grains with c-axes pointing due North (y-direction of the image) have a misorientation of 0°, grains with c-axes in the plane normal to North have a misorientation of 90°. - With color coding, the grains sub-/parallel to North are purple, those in the plane normal to North are green. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
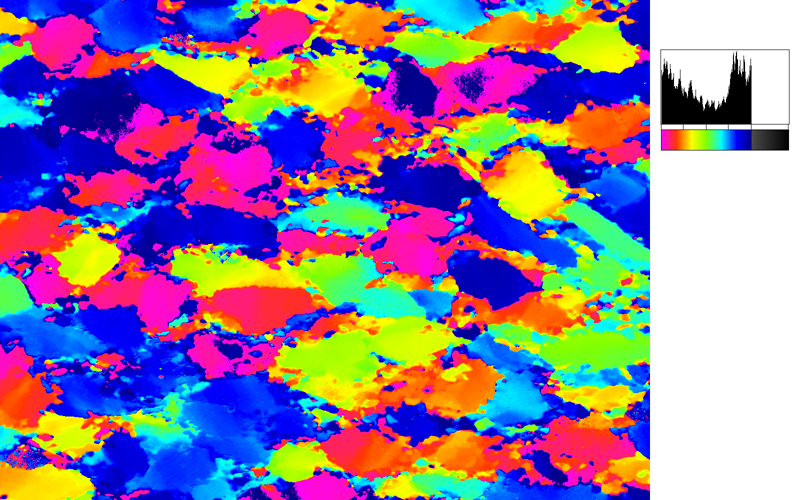
After the CIP calculation, the different result files have to be evaluated. Here, the misorientaion file w/r to North is shown. The values span a range of (0° ≤ angle ≤ 180°). Grains with c-axes pointing due North (y-direction of the image) have a misorientation of 0°, grains with c-axes in the plane normal to North have a misorientation of 90°. - With color coding, the grains sub-/parallel to North are purple, those in the plane normal to North are green. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
GETTING STARTED
Load Lazy CIP LUTs macro.
The macros are grouped in seven groups depending on which orientation images are to be visualized:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
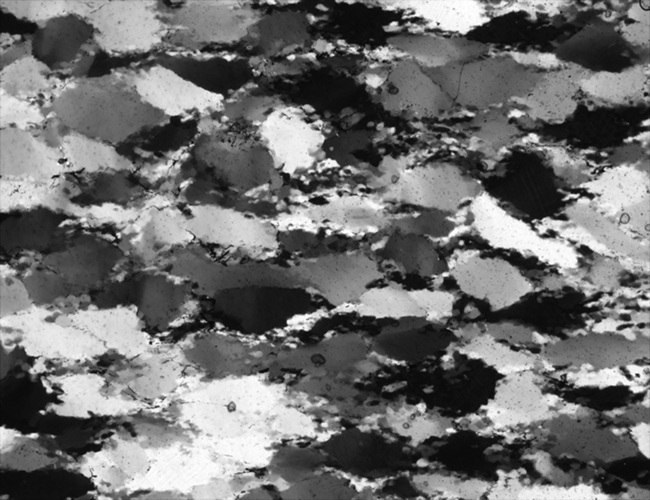

ROT000: rotation image at 0° rotation |
ROT000: presented as crossed polarization with lambda plate inserted
|
A quartz microstructure is shown at the top. Of this sample a CIP calculation is carried out. The CIP misorientation image (COI) with the stereographic CLUT and the pole figure is shown on the right. > |
|||||||||
|
|
|
PREPARING NICE IMAGES AND STACKS
The first group of macros is intended to open images, prepare stacks (e.g., of misorientation images),
to achieve a minimal layout, to insert histograms and gray scales.
|
||||||||
|
|
|
USING ROTATION IMAGES
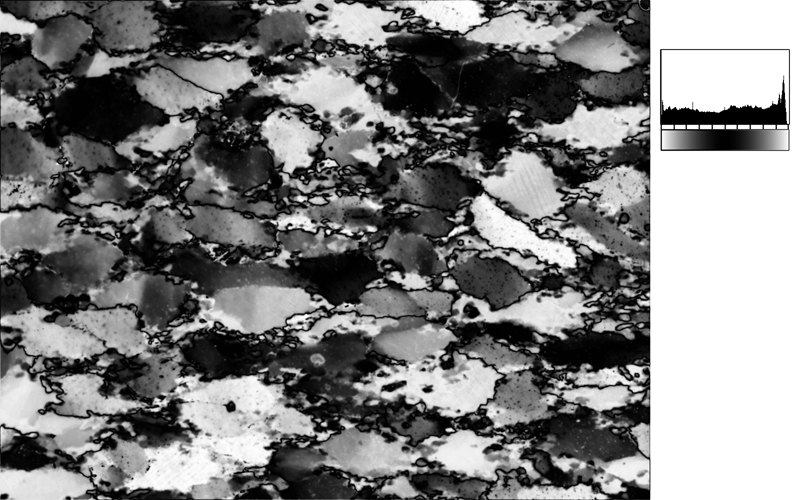
Rotation images are CIP input images.
|
||||||||
|
|
|
USING INCLINATION IMAGESInclination images are CIP output images.
|
||||||||
|
|
|
USING AZIMUTH IMAGESAzimuth images are CIP output images.
|
||||||||
|
|
|
USING MISORIENTATION IMAGESMisorientation images are CIP output images.
|
||||||||
|
|
|
USING ORIENTATION GRADIENT IMAGESOrientation gradient images are CIP output images. Four different types are available:
For better resolution, the average (or maximum) gradient is recorded such that 1° = 2 GV.
|
||||||||